Data is the fuel of digital marketing: without it, your advertising engine won’t run. As privacy regulations and consumer expectations evolve, some data signals are fading away. This means advertisers need to use their first-party data more efficiently to target audiences effectively. Three technologies that help transform raw data into actionable campaign fuel are data management platforms (DMPs), customer data platforms (CDPs), and data clean rooms (DCRs).
Whether you’re new to an agency or a veteran marketer, you may want a refresher on how these data technologies work, the differences between CDPs and DMPs, use cases, and more. Read on for the lowdown on what you need to know about DMPs, CDPs, and data clean rooms.
Data management platforms (DMPs): Build audience segments
DMP stands for data management platform. A DMP is the central command center for your customer data. Think of them like a headquarters where all the data on your target audience is collected from your various sources and ultimately organized into audience segments so that you, the marketer, can make better decisions on your campaigns.
To effectively market their products or services, brands rely on data about their customers and target audience. The DMP organizes and presents this data in digestible ways so that marketers can properly segment audiences for advertising that’s tailored to the interests or behaviors of each segment.
How do DMPs work?
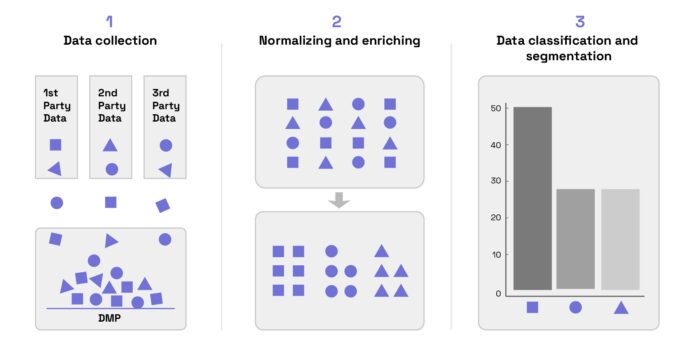
We can break down how DMPs work into three steps: data collection, data normalization and enrichment, and segmentation.
Using a DMP for data collection
A data management platform’s first job is to collect data from all the various sources your brand uses — everything from your own first-party data to second and third party data (which is becoming rarer and more difficult to acquire with recent developments in privacy). To bring all this data together, DMPs typically integrate with other adtech and martech platforms, such as a demand-side platform (DSP), an ad exchange, and a supply-side platform (SSP). DMPs may also connect to a customer relationship management (CRM) system like Hubspot or Salesforce.
Normalizing and enriching data with a DMP
What good are tons of data sets if you’re comparing apples against oranges, bananas, papayas, and kiwis? After data collection, a DMP normalizes the data so we can analyze apples with other apples. Then the DMP enriches this data with additional signals such as device type, device location, browser version, and operating system.
Data classification and segmentation
After data enrichment, it’s ready for segmentation. This is where the DMP groups together data with similar attributes into categories (also called data taxonomies). These classifications make it easier for a marketer to build unique user profiles and create audience segments — groups of individuals with similarities. For example, a DMP can help build an audience segment of women aged 18-34 who have streamed Taylor Swift in the last 12 months.
Customer data platforms (CDPs): Gain a complete view of each customer
Customer data platforms, or CDPs, are quite similar to DMPs in that they also collect customer data and present it for easier decision-making. But unlike DMPs that focus on audience segmentation, CDPs focus on individual customers.
The entire point of the CDP is the unified customer profile, which paints a clearer picture of who your customer really is based on their purchase history, their in-app behavior or website behavior, their preferences, and much more. If you can understand what they like, how they make decisions, and what triggers them to make a purchase, you have the power to influence their actions.
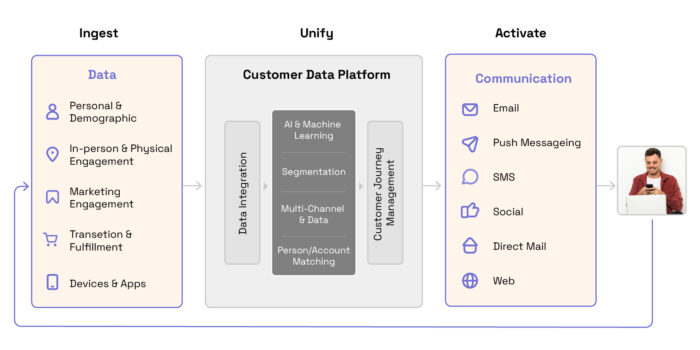
How do CDPs work?
- CDPs use your own customer data (first-party data) from sources as varied as your app, your website, customer relationship management (CRM) system, email subscribers, and even loyalty programs. This CDP capability is sometimes called “data ingestion.”
- Using this first-party data, CDPs store these stitched-together customer profiles so that other stakeholders can access the information for their campaigns.
- Finally, CDPs collate the data to find useful patterns in behavior, providing marketers with insight into what kinds of campaigns might work on these customers. This makes the data ready for activation in campaigns across many channels.
DMP vs. CDP: What’s the difference?
DMPs are typically used to build profiles for anonymous (often, target) users. The most useful outcome from a DMP are audience segments that you can use to market to groups with similar tastes and characteristics.
CDPs are typically used with customers you already have. The most useful outcome here is a complete customer profile that allows you to tailor campaigns to an individual’s behaviors or demographics.
Data clean rooms (DCRs): Shared datasets, better insights
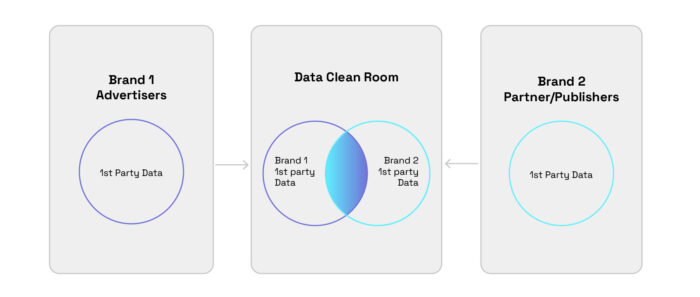
Data clean rooms are tightly controlled environments where multiple organizations (typically an advertiser and a publisher) can safely pool together their customer data, allowing both parties to analyze the combined datasets for insights they couldn’t get otherwise.
This relatively new idea in marketing analytics only works because user privacy is prioritized. In place of personally identifiable information (PII), advanced techniques are used to anonymize the data across datasets. In short, one participant can never see the raw data from another participant.
Note that data clean rooms will never replace a DMP or a CDP. Instead, they complement the work that your DMPs do to build your audience segments, and the work that your CDP does to create unified customer profiles. By enabling you to securely collaborate on combined datasets, data clean rooms allow you to arrive at better insights.
How do data clean rooms work?
-
- Participating organizations collect first-party data – everything from purchase history, to demographics and in-app or website behavior.
- But here’s the most important part: that data has to be anonymized with all PII taken out or encrypted to ensure user privacy.
- Anonymized data is uploaded to the data clean room, which uses advanced algorithms to find matches between the datasets.
- Participating organizations can then set up queries and analyses on the combined data to find patterns or insights, which can be downloaded via reports.
Complementary tools, different goals
When it comes to DMPs vs. CDPs vs. data clean rooms, these aren’t rival technologies. They’re complementary tools that allow the modern marketers to better understand their target audiences. The best choice for you depends on your needs:
-
- Use DMPs for segmenting your audience and for better targeting of your online ads.
- Use CDPs for creating a single, comprehensive view for each customer, giving you the ability to serve up hyper-personalized experiences for an audience of one.
- Use data clean rooms for unlocking deeper audience insights by analyzing anonymized data points from combined datasets with another organization.
Privacy-first targeting
As cookies and identifiers fade away, advertising strategies and ways of using data are evolving. Here at Verve, we’re helping lead the charge with privacy-first advertising solutions that deliver better outcomes with responsible media. To learn more, don’t hesitate to reach out to our team.